Present a design solution through a range of communication techniques appropriate to the target audience.
Before you start please read the following instructions carefully.
1 This assignment forms part of the formal assessment for this module. You should therefore not submit the assignment until you are reasonably sure that you have completed it successfully. Seek your tutor`s advice if unsure.
2 Ensure that you indicate the number of the question you are answering.
3 Make a copy of your answers before submitting the assignment.
4 Complete all details on the front page of this TMA and return it with the completed assignment including supporting calculations where appropriate. The preferred submission is via your TUOL(E) Blackboard account: https://eat.tees.ac.uk
5 Your tutor’s comments on the assignment will be posted on Blackboard
Assessment Criteria
This assignment relates to the production of CAD drawings and a design project.
The assignment forms Element 2 of the module’s assessment criteria that covers Learning Outcomes 1, 4 and 5 as indicated below.
|
MODULE LEARNING OUTCOMES
|
|
Personal & Transferable Skills
On successful completion of this module the student will be able to:
1 Present a design solution through a range of communication techniques appropriate to the target audience.
|
|
Research, Knowledge & Cognitive Skills
2 Prepare design specifications and solutions to meet a stakeholder’s design brief and requirements.
3 Select, apply and justify appropriate approaches, methods and tools to a variety of engineering design problems.
|
|
Professional Skills
4 Produce an industry-standard engineering technical design report.
5 Select and use computer-based technology in the design process.
|
|
PASS
|
MERIT
Criteria in excess of the pass grade.
|
DISTINCTION
Criteria in excess of the merit grade.
|
|
Learning outcomes are
|
Drawings are well detailed
|
Thorough understanding of
|
|
satisfied as evidenced by
|
and represent fully the
|
the subject matter
|
|
CAD drawings and a
|
chosen design solution. An
|
demonstrating awareness in
|
|
satisfactory report.
|
easily navigated report.
|
its context, effect, limitations
|
|
|
|
& potential for improvement.
|
|
|
|
Report has no major
|
|
|
|
technical or structural flaws.
|
1 Following on from the first TMA in this module, produce a design report for one design of the product based on one of the scenarios covered on the following pages. The report should contain, where appropriate:
- Title page
- Acknowledgements
- Summary
- Contents
- Introduction
- Basic Product Design Specification
- Design Parameters
- Simple Description of chosen Design
- Design Evaluation
- Detailed drawings of the design, including dimensions, such that its constructional features can be seen*
- Conclusions
- References
- Appendices
* Drawings should be submitted as complete engineering drawings done using CAD (or other suitable software). If the maximum size of printing is A4 then several sheets, each showing a different view of the design, will probably be needed to show sufficient detail for the design to be constructed. In this case, all views should be clearly labelled and all sheets numbered. Only computer-produced drawings will be marked; it is not acceptable to submit hand-drawn work. Please submit copies of the drawings within the report (.PDF) and in addition, upload the computer files of the drawings (.DWG).
Note: you may have to invent information to make the design report complete
SCENARIOS
Either
(a) Bicycle Rack
When a full design specification was produced and the weighted objective procedure carried out, it was found that a tow bar mounted rack was the best solution.
The rack is to bolt to the tow bar once the tow ball is removed. The dimensions of the tow bar bracket are shown in Figure 1. The 330 mm dimension refers to the distance from the ground to the bottom of the bracket. In order to avoid the bikes fouling the car, it should be assumed that no part of either bike should protrude beyond the face of the tow bar bracket (ie between the bracket and the car).
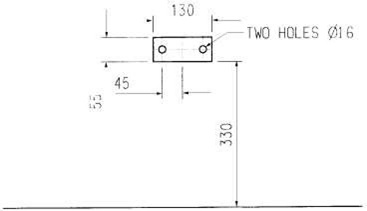
Figure 1
The two bikes to be carried have dimensions shown in Figures 2 and 3. The width of the handlebars of the man’s bike is 420 mm, whilst that of the woman’s is 630 mm. The width across the pedals is 360 mm in both cases.
Your good friend Fred has offered to help build the bike rack and he has access to the following materials and equipment:
- square section steel tubing, 25 mm × 25 mm × 2 mm thick
- steel plate, 8 mm thick
- steel strips, 25 mm wide by 6mm thick
- brazing and welding gear
- a powered hacksaw
- a pillar drill
Design a suitable rack that can be made using Fred’s materials and equipment. It is not necessary to worry about stresses: the materials are capable of exceeding the strength requirements of any design. In addition, the rack should be designed to ‘look right’.
As part of the report, you should produce:
(i) An arrangement drawing showing the outline of the bikes on the rack. This does not need to be very detailed or show any dimensions but should clearly demonstrate that the rack will enable the two bikes to be carried without fouling the car or the ground.
(ii) A detailed engineering drawing of the rack only, comprising front and side elevations with all dimensions required for manufacture shown.
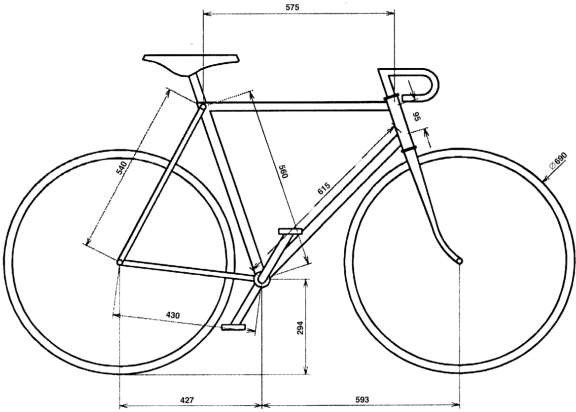
Figure 2 - Man`s Bike
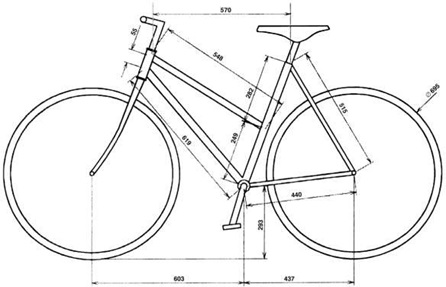
Figure 3 – Woman’s Bike
OR
(b) Front Panel of Circuit Trainer
An analogue/digital circuit trainer is required for open-learning students to use to build circuits as part of their electrical/electronic practical work.
The circuits to be built can consist of up to five integrated circuits and their associated discrete components.
Figures 4, 5 and 6 show block diagrams for each system of the intended design.
(i) A power supply consisting of:
- 240 V supply input
- power ‘on’ indicator
• +5 V output
• +12 V output
- –12 V output
- 0 to +12 V variable output
- 0 to –12 V variable output
- output short-circuit indicators for ‘+’ and ‘–’ supplies
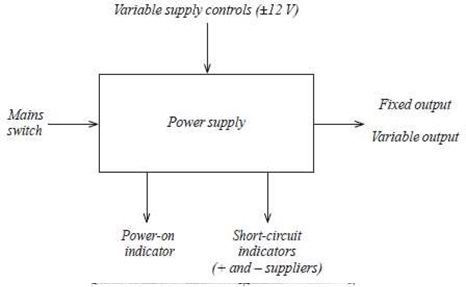
Figure 4
(ii) A function generator capable of:
- generating sinusoidal, triangular and square waveforms
- variable amplitude
- variable frequency
- frequencies in the ranges 0 to 100 Hz, 100 Hz to10 kHz and 10 kHz to 1 MHz
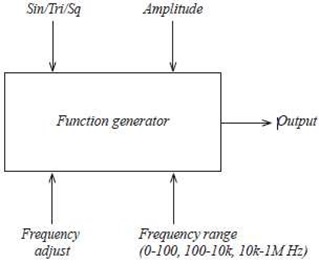
Figure 5
(iii) A multimeter capable of measuring:
- resistance
- voltage
- current
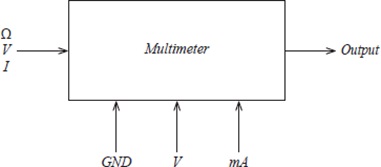
Figure 6
You will be required to draw a plan view of the front panel to show the mounting of the various controls, etc. A photograph of an example of an existing circuit trainer is given in Figure 7.

Figure 7
- END OF QUESTIONS -
100% Plagiarism Free & Custom Written,
tailored to your instructions